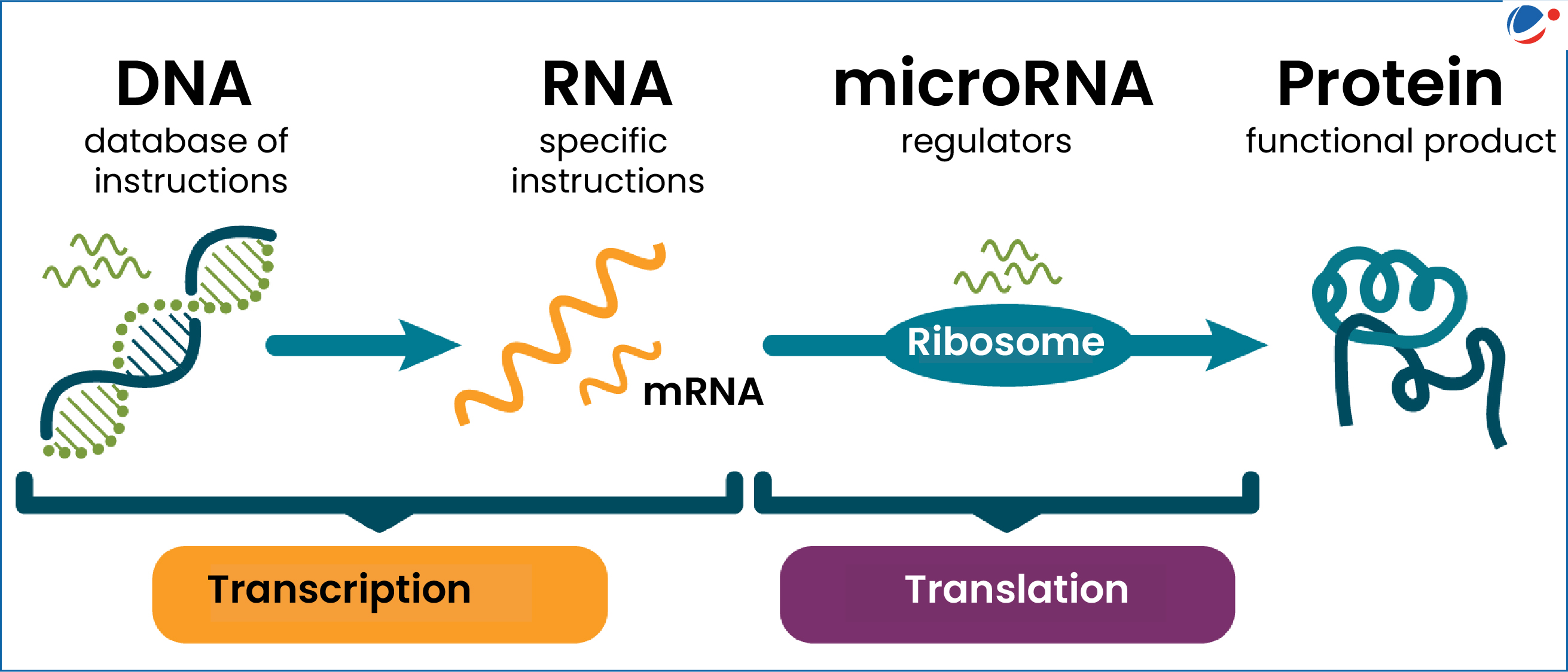
The remarkable journey of microRNA discovery, pioneered by Gary Ruvkun and his team in the early 1990s, has transformed our understanding of gene regulation and earned Ruvkun the prestigious 2024 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine. Initially met with skepticism, their groundbreaking findings regarding the role of microRNAs in the C. elegans roundworm opened up new avenues in RNA research, ultimately influencing the way scientists comprehend genetic expression across various species, including humans. With the backing of federal funding research, Ruvkun’s studies illustrated the significance of these tiny RNA molecules in regulating protein production, fundamentally altering the landscape of molecular biology. The exploration into RNA therapeutics has since burgeoned, with numerous clinical trials underway targeting ailments such as cancer and heart disease. As the landscape of genetic research continues to evolve, Ruvkun’s contributions remain pivotal in pushing the boundaries of medical science and therapy.
The exploration of microRNAs represents a crucial milestone in genetic research, shedding light on intricate mechanisms of gene expression and cell regulation. Gary Ruvkun’s pioneering efforts in uncovering these small RNA molecules have sparked a wide array of advancements in the field, influencing everything from fundamental science to pharmaceutical innovations. The journey from initial discoveries in model organisms to potential applications in human health highlights the significance of federal support and funding for scientific research. This concept of small, regulatory RNA not only enhances our understanding of biology but also opens up new pathways for developing targeted treatments. As the conversation around RNA therapies expands, the ongoing relevance of microRNAs and their regulatory functions continues to captivate researchers and medical professionals alike.
The Revolutionary Impact of microRNA Discovery
In 1992, Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros’s discovery of microRNA marked a turning point in the field of genetics and molecular biology. This tiny RNA molecule offered new insights into gene regulation, revealing mechanisms that control the expression of genes in organisms as varied as the C. elegans roundworm and humans. Although the initial reception of their findings was tepid, the long-term implications of their work have since transformed our understanding of biology. The capability of microRNAs to influence gene expression plays a pivotal role in numerous biological processes, which explains their recognition with the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
MicroRNA research has flourished over the decades, leading to groundbreaking applications in RNA therapeutics. As Ruvkun noted, the gradual accumulation of interest in microRNAs has led to enhanced collaboration among scientists, expanding its significance across various biological disciplines. Today, it is clear that microRNAs are not just minor players but central components in the translational process of genes to proteins, ultimately affecting how organisms grow, develop, and respond to diseases.
The Role of Federal Funding in Scientific Research
For over four decades, Gary Ruvkun has attributed a significant portion of his research success to federal funding, particularly through programs offered by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). With annual grants averaging around $150,000, Ruvkun has managed to maintain a small but effective laboratory that has contributed to critical discoveries in genetics. He argues that federal support is essential for fostering basic research that drives innovation, technological advancement, and ultimately, economic growth. The long-term benefits of such investments cannot be overlooked, as they contribute to a knowledgeable workforce and a thriving scientific community.
Despite these successes, Ruvkun expresses concern over recent trends advocating for cuts in federal research funding. He highlights that a reduction in investments could deter young scientists from pursuing careers in research, potentially stifling the next generation of innovation. The historical context is crucial—federal funding has been a backbone of America’s scientific advancement since World War II, establishing the country as a leader in technological progress. As Ruvkun observes, threats to this support system could compel emerging scientists to seek opportunities abroad, exacerbating the talent drain from the U.S. scientific landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of microRNA discovery in gene regulation?
The discovery of microRNA (miRNA) is crucial in understanding gene regulation as it introduces a new layer of control over gene expression. This small RNA molecule can bind to messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and inhibit their translation into proteins, thus playing a fundamental role in cellular processes such as development, growth, and response to environmental signals.
How did Gary Ruvkun contribute to the field of microRNA research?
Gary Ruvkun, along with Victor Ambros, was pivotal in the discovery of microRNA in the early 1990s. Their research identified miRNA’s role in gene regulation within the C. elegans model organism, paving the way for future studies showing that these tiny RNAs are essential across various species, including humans.
What role does federal funding play in microRNA research?
Federal funding, particularly from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), has been instrumental in facilitating groundbreaking research in microRNA. Gary Ruvkun’s lab, for example, has relied on federal grants for about 75% of its funding over the past four decades, which has underpinned significant advancements in understanding RNA and its therapeutic applications.
What potential do microRNA therapeutics have for treating diseases?
MicroRNA therapeutics hold great promise for treating various diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s. These therapies are currently in clinical trials and aim to leverage the regulatory capabilities of miRNAs to correct gene expression and improve therapeutic outcomes.
How has the perception of microRNA evolved since its discovery?
Since its discovery in the early 1990s, the perception of microRNA has transformed dramatically. Initially, the scientific community was skeptical about its relevance; however, as research demonstrated miRNA’s crucial role in gene regulation across diverse organisms, interest surged, resulting in a robust field of study that underpins modern genetics and biotechnology.
What impact did Gary Ruvkun’s discovery of microRNA have on the pharmaceutical industry?
Gary Ruvkun’s discovery of microRNA has significantly influenced the pharmaceutical industry by laying the groundwork for RNA interference therapeutics, as seen with companies like Alnylam. These advancements have led to the development of innovative treatments for genetic diseases, demonstrating the profound impact that basic science can have on medicine and industry.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Discovery of microRNA by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros in 1992, resulted in the 2024 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine. |
| Initial lack of recognition for their findings, even after publishing in Cell in 1993. |
| Growing interest in microRNA research as its significance across species became clearer over time. |
| MicroRNAs play a crucial role in gene regulation and are involved in numerous biological processes and diseases. |
| Approximately 1,000 microRNAs are found in the human genome, influencing protein production and related therapies. |
| Federal funding has been instrumental in supporting ongoing research in this area, emphasizing the importance of continued investment. |
| Ruvkun highlights the need for sustained federal support to keep talented individuals in scientific research in the U.S. |
Summary
MicroRNA discovery marked a pivotal advancement in genetics, as it unfolded the complexities of gene regulation that are crucial for understanding various biological functions. The journey from the initial discovery by Ruvkun and Ambros in 1992 to their eventual recognition with the Nobel Prize in 2024 underlines the importance of persistent research and federal funding in scientific progress. The impact of microRNAs is profound, affecting not only gene expression but also promising therapeutic avenues for multiple diseases, reinforcing the significance of the ongoing support for research in this vital field.